The logistics industry stands at the threshold of a transformative era, where autonomous vehicles and advanced connectivity are reshaping how goods move across regional networks and beyond.
🚛 The Dawn of Autonomous Logistics Revolution
Regional logistics has long been the backbone of economic activity, connecting manufacturers with distributors, retailers with consumers, and businesses with their supply chains. However, traditional logistics systems face mounting pressures from rising operational costs, driver shortages, environmental concerns, and increasing customer expectations for faster delivery times. The convergence of autonomous technology and seamless connectivity offers unprecedented opportunities to address these challenges while revolutionizing the entire logistics ecosystem.
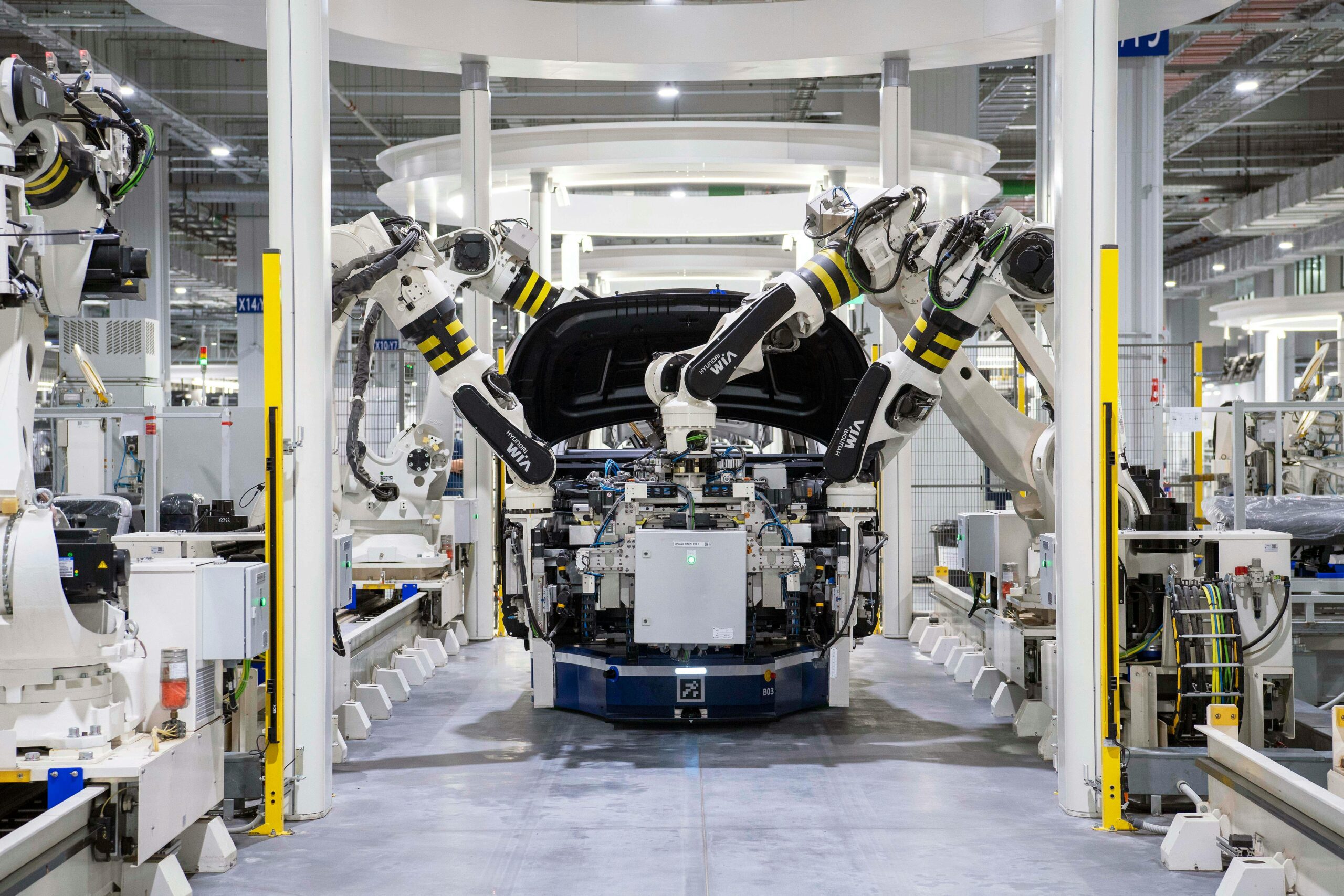
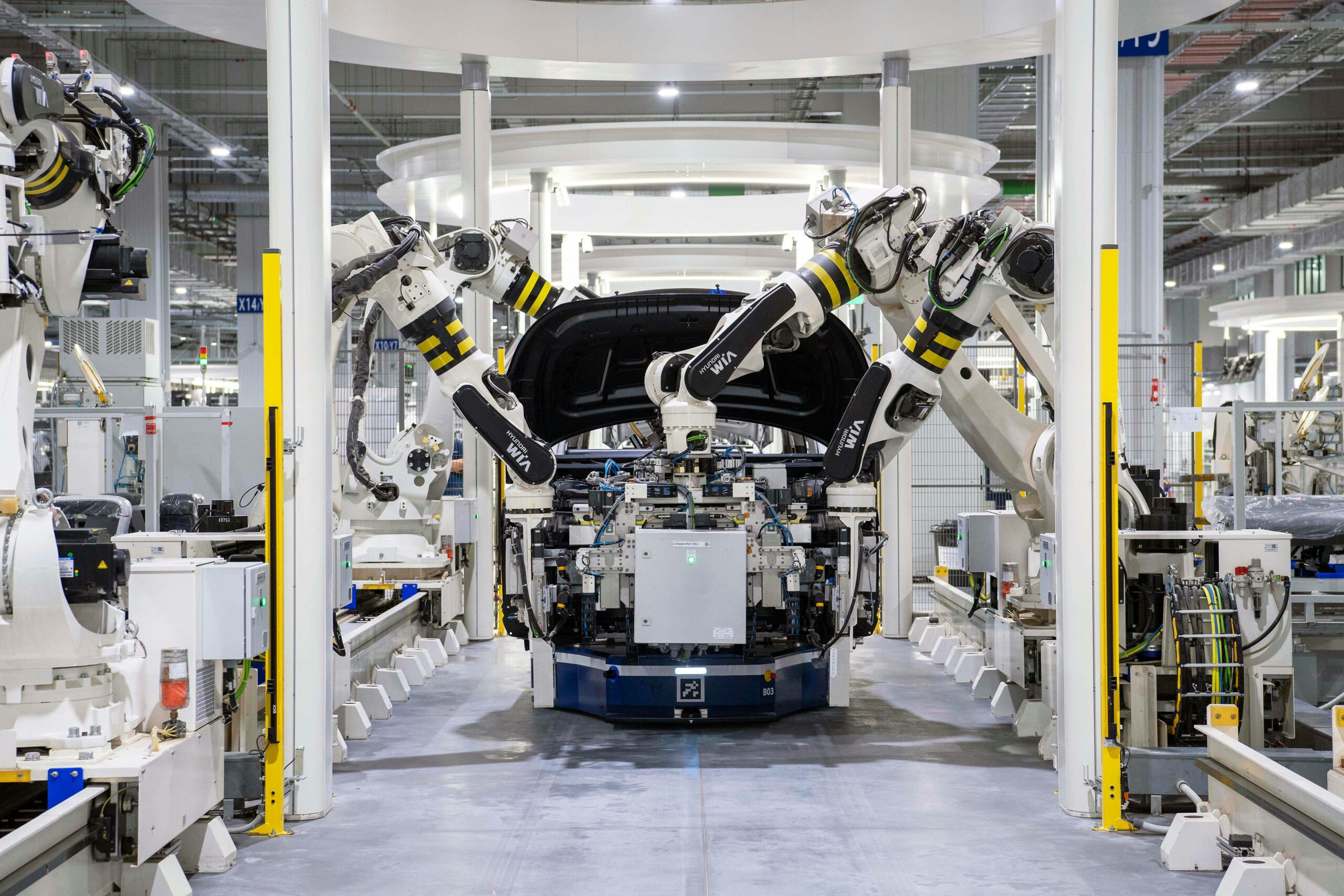
Autonomous innovation in logistics extends far beyond self-driving trucks. It encompasses a comprehensive ecosystem of intelligent systems, including automated warehouses, drone deliveries, predictive analytics, and interconnected supply chain networks. These technologies work in concert to create a logistics infrastructure that is more efficient, reliable, and responsive than ever before.
Understanding the Autonomous Logistics Landscape
The autonomous logistics revolution is built upon several key technological pillars that work together to create seamless operations. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms process vast amounts of data to optimize routes, predict maintenance needs, and make real-time decisions that enhance operational efficiency. Advanced sensor technologies, including LiDAR, radar, and high-resolution cameras, enable vehicles to perceive their environment with unprecedented accuracy.
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication systems allow autonomous vehicles to interact with infrastructure, other vehicles, and central management systems, creating a coordinated network that responds dynamically to changing conditions. Edge computing capabilities enable rapid data processing at the source, reducing latency and enabling split-second decision-making critical for safe autonomous operations.
The Technology Stack Powering Innovation
Modern autonomous logistics systems integrate multiple layers of technology to deliver reliable performance. At the foundation lies robust hardware including specialized processors designed for autonomous operations, redundant sensor arrays for safety, and advanced battery systems or alternative power sources for extended range and reliability.
The software layer encompasses sophisticated perception algorithms that interpret sensor data, path planning systems that navigate complex environments, and decision-making frameworks that handle unexpected situations. Cloud-based platforms provide centralized management, enabling fleet operators to monitor operations, analyze performance data, and deploy updates across entire networks simultaneously.
🌐 Seamless Connectivity as the Nervous System
Connectivity serves as the nervous system of autonomous logistics networks, enabling real-time communication, coordination, and control. The rollout of 5G networks with their ultra-low latency and high bandwidth capabilities provides the infrastructure necessary for autonomous vehicles to communicate effectively with central management systems and each other.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices embedded throughout the logistics chain provide continuous visibility into shipment locations, condition monitoring, and environmental factors. This comprehensive data ecosystem enables predictive analytics that anticipate problems before they occur, optimize resource allocation, and provide customers with unprecedented transparency into their supply chains.
Building Resilient Communication Networks
Redundancy and reliability are paramount in autonomous logistics communication systems. Advanced networks employ multiple communication pathways, including cellular networks, satellite connections, and dedicated short-range communications (DSRC), ensuring continuous connectivity even in challenging environments or during network disruptions.
Edge computing nodes positioned strategically throughout regional networks process critical data locally, reducing dependence on constant cloud connectivity while maintaining the benefits of centralized coordination. This distributed architecture enhances system resilience and enables operations to continue safely even during temporary communication interruptions.
Regional Logistics: The Perfect Testing Ground
Regional logistics operations provide an ideal environment for implementing autonomous innovation. Unlike long-haul routes that cross diverse jurisdictions and challenging terrains, regional networks typically operate within more controlled environments with familiar routes, predictable traffic patterns, and established infrastructure relationships.
The shorter distances and frequent stops characteristic of regional logistics align well with current autonomous vehicle capabilities and charging infrastructure availability. Fleet operators can implement autonomous systems incrementally, starting with specific routes or facilities before expanding to broader networks as technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve.
Operational Advantages in Regional Networks
Autonomous systems excel in the repetitive, predictable nature of many regional logistics operations. Automated vehicles can operate continuously without fatigue-related limitations, dramatically increasing asset utilization. A truck that traditionally operates eight to ten hours daily can potentially triple its productive time, significantly improving return on investment.
Labor shortages plaguing the logistics industry become less constraining as autonomous systems supplement and eventually replace traditional staffing models. Human workers can transition to supervisory, maintenance, and exception-handling roles that leverage uniquely human capabilities while autonomous systems handle routine operations.
💡 Transforming the Last Mile Challenge
The last mile represents both the most expensive and most challenging segment of logistics operations. Autonomous delivery solutions ranging from sidewalk robots to autonomous vans are revolutionizing this critical final connection between distribution centers and customers.
Delivery robots navigate sidewalks and crosswalks, transporting packages directly to customer doorsteps with minimal human intervention. These systems are particularly effective in urban environments where parking challenges and traffic congestion make traditional delivery methods increasingly inefficient and expensive.
Drone Delivery Integration
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) complement ground-based autonomous systems by providing rapid delivery options for time-sensitive or remote destinations. Drone delivery networks are particularly valuable in regional logistics, where they can efficiently serve suburban and rural areas that pose economic challenges for traditional delivery methods.
Integration of drone operations with ground-based logistics networks creates flexible, multi-modal delivery systems that optimize routes and methods based on package characteristics, delivery urgency, and geographic considerations. Automated coordination between different delivery modes ensures seamless customer experiences while maximizing operational efficiency.
Safety and Security in Autonomous Operations
Safety remains the paramount concern in autonomous logistics implementation. Modern systems incorporate multiple redundant safety mechanisms, including backup sensors, fail-safe systems that bring vehicles to safe stops during malfunctions, and continuous monitoring by remote operators who can intervene when necessary.
Cybersecurity measures protect autonomous systems from potential threats, including encrypted communications, secure software update mechanisms, and intrusion detection systems that identify and respond to potential security breaches. Regular security audits and updates ensure systems remain protected against evolving threats.
Building Public Trust Through Performance
Public acceptance of autonomous logistics systems depends on consistent, safe performance over extended periods. Transparent reporting of safety metrics, proactive communication about system capabilities and limitations, and demonstrated commitment to continuous improvement help build the trust necessary for widespread adoption.
Collaboration with regulatory agencies, community stakeholders, and industry partners ensures autonomous systems are deployed responsibly and meet appropriate safety standards. Pilot programs in controlled environments provide opportunities to demonstrate capabilities and refine systems before broader deployment.
📊 Economic Impact and Business Models
The economic implications of autonomous logistics extend throughout supply chains and regional economies. Initial capital investments in autonomous systems are substantial, but operational savings from reduced labor costs, improved fuel efficiency, and enhanced asset utilization typically generate positive returns within predictable timeframes.
New business models emerge as autonomous capabilities mature. Logistics-as-a-service offerings provide flexible capacity without capital investment, appealing to businesses seeking agility. Shared autonomous logistics networks enable smaller companies to access sophisticated capabilities previously available only to large enterprises.
Workforce Transformation and Opportunities
While autonomous systems reduce demand for traditional driving positions, they create new opportunities in system operation, maintenance, data analysis, and customer service. Successful transitions require proactive workforce development programs that help existing employees acquire skills relevant to the autonomous logistics environment.
Technical positions supporting autonomous systems typically offer higher wages and better working conditions than traditional logistics roles, potentially attracting new talent to the industry. Education partnerships with technical schools and universities help develop pipelines of skilled workers prepared for autonomous logistics careers.
🌍 Environmental Sustainability Benefits
Autonomous logistics systems contribute significantly to environmental sustainability goals. Optimized routing reduces unnecessary mileage and fuel consumption, while smooth, efficient driving patterns made possible by autonomous systems improve fuel efficiency compared to human drivers.
Electric powertrains integrate naturally with autonomous systems, and the combination delivers substantial emissions reductions. Autonomous systems can optimize charging schedules based on grid demand and renewable energy availability, further enhancing environmental benefits.
Reducing Urban Congestion and Emissions
Coordinated autonomous logistics networks reduce traffic congestion by optimizing delivery times and consolidating shipments. Off-peak delivery capabilities enabled by autonomous operations shift logistics traffic away from congested periods, improving overall urban traffic flow.
Smaller, right-sized autonomous delivery vehicles reduce the number of large trucks in urban areas, decreasing both congestion and local emissions. Purpose-built autonomous delivery vehicles optimize cargo capacity and vehicle size for specific applications, eliminating the inefficiency of using oversized vehicles for small deliveries.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standardization
Successful autonomous logistics deployment requires supportive regulatory frameworks that balance innovation with safety and public interest. Progressive jurisdictions are developing regulations that enable autonomous operations while maintaining appropriate oversight and accountability.
Industry standardization efforts ensure interoperability between systems from different manufacturers and compatibility with infrastructure investments. Common communication protocols, safety standards, and data formats enable the integrated logistics ecosystems necessary for realizing the full potential of autonomous innovation.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape
Logistics companies implementing autonomous systems must actively engage with regulatory processes, providing input based on operational experience while demonstrating commitment to safety and public welfare. Collaborative relationships with regulators facilitate the development of practical frameworks that enable innovation while protecting public interests.
Harmonization of regulations across jurisdictions reduces complexity and enables efficient regional operations. Industry associations and collaborative initiatives work to identify best practices and promote consistent approaches to autonomous logistics regulation.
🚀 The Road Ahead: Future Innovations
The autonomous logistics revolution continues accelerating as technologies mature and adoption expands. Artificial intelligence capabilities improve continuously, enabling systems to handle increasingly complex scenarios and edge cases that previously required human intervention.
Vehicle technology advances toward fully autonomous Level 5 operations that require no human intervention under any conditions. While regulatory and technical challenges remain, the trajectory toward comprehensive autonomous capabilities is clear.
Integration with Smart Infrastructure
Future logistics networks will integrate seamlessly with smart city infrastructure, including intelligent traffic management systems, automated loading facilities, and dynamic routing systems that respond to real-time conditions. This infrastructure co-evolution amplifies the benefits of autonomous systems and enables capabilities impossible with vehicles or infrastructure operating independently.
Blockchain and distributed ledger technologies provide transparent, secure tracking and verification throughout supply chains, enhancing accountability and enabling new collaboration models. Smart contracts automatically execute logistics transactions when predefined conditions are met, reducing administrative overhead and accelerating operations.
Collaborative Ecosystems Driving Innovation
No single organization can realize the full potential of autonomous logistics alone. Successful implementation requires collaboration among vehicle manufacturers, technology providers, logistics operators, infrastructure owners, and regulatory agencies. Industry consortiums facilitate knowledge sharing, establish standards, and coordinate investments in shared infrastructure.
Open innovation models accelerate development by enabling specialized companies to contribute innovations to the broader ecosystem. Application programming interfaces (APIs) and platform architectures allow best-of-breed solutions to integrate seamlessly, creating comprehensive systems that leverage the strengths of multiple providers.
⚡ Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Despite tremendous promise, autonomous logistics faces significant implementation challenges. Technical limitations remain in handling complex scenarios, adverse weather conditions, and unpredictable human behaviors. Continued research and development address these limitations, steadily expanding the operational envelope of autonomous systems.
Infrastructure investments required to support autonomous operations represent substantial commitments, particularly for smaller logistics operators. Public-private partnerships can help distribute these costs while ensuring infrastructure developments serve broader community interests beyond specific commercial applications.
Change management within organizations implementing autonomous systems requires careful planning and execution. Successful transitions address cultural resistance, provide adequate training and support, and communicate clearly about how autonomous systems will affect roles and responsibilities.
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Effective performance measurement systems track key metrics including safety records, operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and environmental impact. Transparent reporting of these metrics builds stakeholder confidence and identifies opportunities for improvement.
Continuous improvement processes analyze performance data to identify optimization opportunities and refine system operations. Machine learning systems improve autonomously through experience, but human oversight ensures improvements align with organizational objectives and safety requirements.
Benchmarking against industry standards and competitors drives performance improvements and helps organizations identify best practices worth adopting. Collaborative industry initiatives share anonymized performance data, enabling sector-wide learning and advancement.

🎯 Creating Competitive Advantage Through Innovation
Early adopters of autonomous logistics technologies gain significant competitive advantages through improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer service capabilities, and reduced costs. These benefits compound over time as organizations develop expertise and optimize systems for their specific operational contexts.
Strategic implementation of autonomous systems requires alignment with broader business objectives and careful consideration of which operations offer the greatest benefits from automation. Phased deployment approaches manage risks while building organizational capabilities and stakeholder confidence.
Customer experience improvements enabled by autonomous systems including real-time tracking, flexible delivery options, and improved reliability create differentiation in competitive markets. Logistics providers that effectively leverage autonomous technologies position themselves as innovation leaders and preferred partners.
The transformation of regional logistics through autonomous innovation and seamless connectivity represents one of the most significant technological shifts in transportation history. Organizations that embrace these changes thoughtfully and strategically will thrive in the autonomous logistics era, while those that resist adaptation risk obsolescence in an increasingly automated world. The future of logistics is autonomous, connected, and arriving faster than many anticipate. Success requires vision, investment, collaboration, and commitment to continuous innovation as technologies and capabilities continue evolving.
Toni Santos is a systems analyst and resilience strategist specializing in the study of dual-production architectures, decentralized logistics networks, and the strategic frameworks embedded in supply continuity planning. Through an interdisciplinary and risk-focused lens, Toni investigates how organizations encode redundancy, agility, and resilience into operational systems — across sectors, geographies, and critical infrastructures. His work is grounded in a fascination with supply chains not only as networks, but as carriers of strategic depth. From dual-production system design to logistics decentralization and strategic stockpile modeling, Toni uncovers the structural and operational tools through which organizations safeguard their capacity against disruption and volatility. With a background in operations research and vulnerability assessment, Toni blends quantitative analysis with strategic planning to reveal how resilience frameworks shape continuity, preserve capability, and encode adaptive capacity. As the creative mind behind pyrinexx, Toni curates system architectures, resilience case studies, and vulnerability analyses that revive the deep operational ties between redundancy, foresight, and strategic preparedness. His work is a tribute to: The operational resilience of Dual-Production System Frameworks The distributed agility of Logistics Decentralization Models The foresight embedded in Strategic Stockpiling Analysis The layered strategic logic of Vulnerability Mitigation Frameworks Whether you're a supply chain strategist, resilience researcher, or curious architect of operational continuity, Toni invites you to explore the hidden foundations of system resilience — one node, one pathway, one safeguard at a time.